PATENTS
Method And Apparatus For Controlling Catheter Positioning And Orientation
Patent Number: US 2008/0249395 Al
Date Filed: October 9, 2008
Country Filed In: USA
Product Application: CGCI
Description:
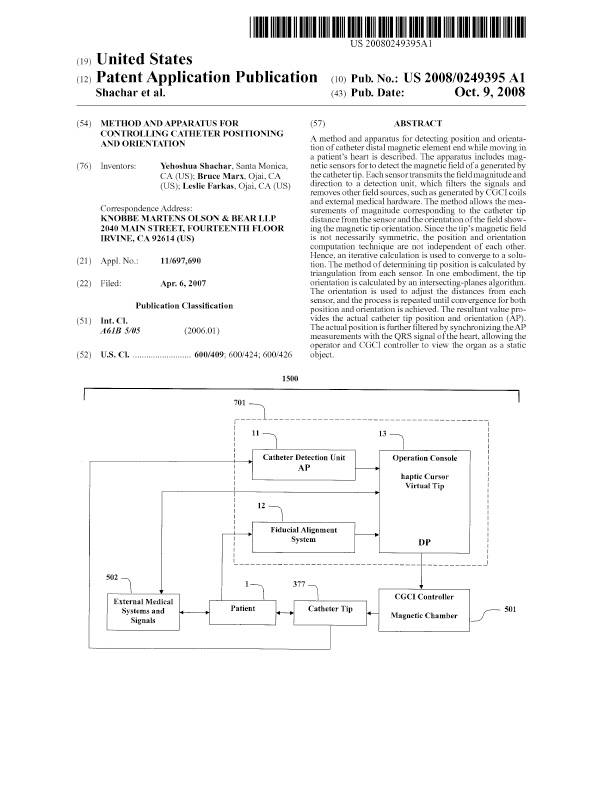
A method and apparatus for detecting position and orientation of catheter distal magnetic element end while moving in a patient's heart are described. The apparatus includes magnetic sensors to detect the magnetic field generated by the catheter tip. Each sensor transmits the field magnitude and direction to a detection unit, which filters the signals and removes other field sources, such as those generated by CGCI coils and external medical hardware. The method allows the measurements of magnitude corresponding to the catheter tip distance from the sensor and the orientation of the field showing the magnetic tip orientation. Since the tip's magnetic field is not necessarily symmetric, the position and orientation computation techniques are not independent of each other. Hence, an iterative calculation is used to converge to a solution. The method of determining tip position is calculated by triangulation from each sensor. In one embodiment, the tip orientation is calculated by an intersecting-planes algorithm. The orientation is used to adjust the distances from each sensor, and the process is repeated until convergence for both position and orientation is achieved. The resultant value provides the actual catheter tip position and orientation (AP). The actual position is further filtered by synchronizing the AP measurements with the QRS signal of the heart, allowing the operator and CGCI controller to view the organ as a static object.
Field of Use: The Catheter Guidance Control and Imaging (CGCI) system was created to provide physicians the ability to guide a catheter through a patient's body using a robotically-controlled magnetic guidance system. Such a system provides the physician unprecedented accuracy in being able to navigate within the dynamic environment of the patient, create a detailed 3-D mapping, and perform a variety of catheter-based operations with precision control and an ability to return to target at the push of a button. Initial applications for the technology were for the field of Electrophysiology and specifically for the ablation of the heart to treat patients with AFib.