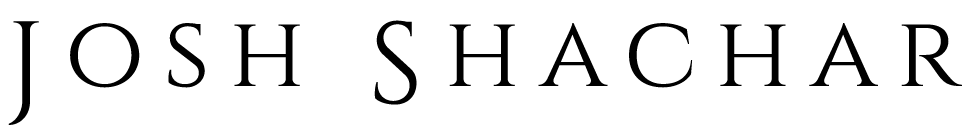RESEARCH PAPERS
Non-Fluoroscopic Transseptal Catheterization During Electrophysiology Procedures using a Remote Magnetic Navigation System
PUBLISHED: December 2013, Journal of Atrial Fibrillation
This paper examined a new technique for non-fluoroscopic re-crossing the fossa ovalis using a new multielectrode transseptal sheath (TS) using the CGCI System. In the study, Transseptal re-crossing was successfully performed in all patients using both the “automated” RMNS-guided technique and the “manual” RMNS-guided technique without complications. The study showed that the CGCI could successfully perform non-fluoroscopic transseptal catheterization.
Development of the Metronomic Biofeedback Pump for Leptomeningeal Carcinomatosis: Technical Note
PUBLISHED: August 2016, Journal of Neurosurgery
This paper looked at Pharmaco-Kinesiss Metronomic Biofeedback Pump’s (MBP) ability to provide a better method for delivery of MTX for the treatment of Leptomeningeal Carcinomatosis. In addition, the paper looks at the MBP’s ability to provide spectrophotometer monitoring, real-time intrathecal MTX concentrations via CSF aspiration, and biofeedback with the possibility of instant control and delivery adjustments.
Dynamically Shaped Magnetic Fields
PUBLISHED: May 26, 2011 Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol
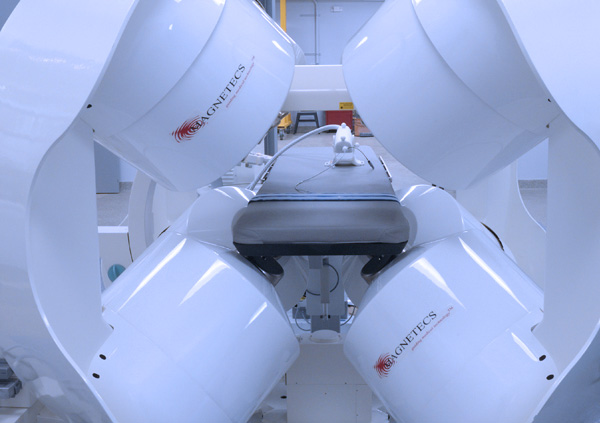
This paper addressed some of the shortcomings of the existing remote catheter navigation systems (RNS) being used at the time. The proposal was to demonstrate the ability of a new magnetic RNS using a dynamically shaped magnetic field concept that could reproducibly and effectively reach target radiofrequency ablation points in a test animal heart. The results of the research in this paper was foundational to the development of the CGCI system.
The Use Of Local Amplifier And MOSFET Sensor Array
PUBLISHED: January 2018
This paper examined the benefits of using a MOSFET Sensor array catheter in electrophysiology applications (EP). The MOSFET catheter has the unique advantage of reliably improving the reading of bioelectric signals by amplifying the signal at the distal end of the catheter thereby dramatically reducing the signal-to-noise ratio issues that traditional EP catheters produced. The results of this study show a vast improvement in dynamic range detection with a much lower signal-to-noise ratio.
Transseptal Catheterization Using A Remote Magnetic Navigation System
PUBLISHED: December 2013 Journal Of Atrial Fibrillation
This paper showed how the CGCI system offered a wholly new method for performing transseptal punctures for left atrial access for complex electrophysiology (EP) procedures such as Afib ablation. In the study, 5 patients underwent repeat transseptal crossing during left-sided ablation procedures using the CGCI system. A total of 11 repeat crossings were performed with the RMNS “automated magnetic” technique, while 15 re-crossings were performed using the “manual magnetic” technique.
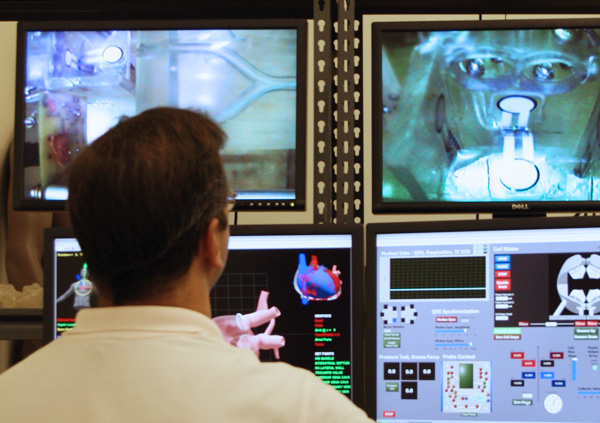
Remote Magnetic Navigation For Ablation In Cardiac Electrophysiology Procedures
PUBLISHED: April 21, 2013 Journal Of Visualized Experiments
This paper was the first clinical report demonstrating the CGCI remote navigation system. The paper details the technical features of the system and its benefits in assisting physicians in the Electrophysiology field for procedures such as ablation in the right and left atrial substrates.